
SBS-IF patients may be on long-term home parenteral support (PS) or parenteral nutrition (PN). PS may include PN and/or any combination with intravenous (IV) fluids.
Components of PN
Energy sources for HPN prescriptions can be derived either from a combined carbohydrate and fat emulsion administered together or from separate glucose and fat emulsion HPN prescriptions delivered on different days.
Many stable patients on HPN are maintained on 20–35 kcals total energy per kg per day.
HPN patients should have optimal blood glucose control, based on blood glucose below 180 mg/dl (10.0 mmol/L) during HPN infusion and normal HbA1c levels (if diabetic), through regular monitoring.
Blood glucose targets should be fasting <7 mmol/L (<140 mg/dl), preinfusion/meals between 4 and 7 mmol/L (100e140 mg/dl), and during HPN infusion 7–10 mmol/L (140e180 mg/dl).
Patients who are not receiving enough nutrition from eating food or who are not able to eat normally are in the group at high risk to develop essential fatty acid (EFA) deficiency if not given an external source of EFA. The necessary minimum of lipid emulsion that should be administered to prevent EFA deficiency is 1 g/kg/week.
Most patients on long-term (>6 months) HPN for CIF without ongoing metabolic complications can be treated with provision of no more than 1 g/kg/day of intravenous soybean-based lipid emulsion.
The following are fluid and electrolyte recommendations for parenteral nutrition:

*Adjustments may be needed for underlying disease, clinical case, medications, and oral intake.
Clinical signs and symptoms as well as biochemical indexes of vitamin deficiency or toxicity should be regularly evaluated.
Clinical signs and symptoms as well as biochemical indexes of trace element deficiency or toxicity should be regularly evaluated.
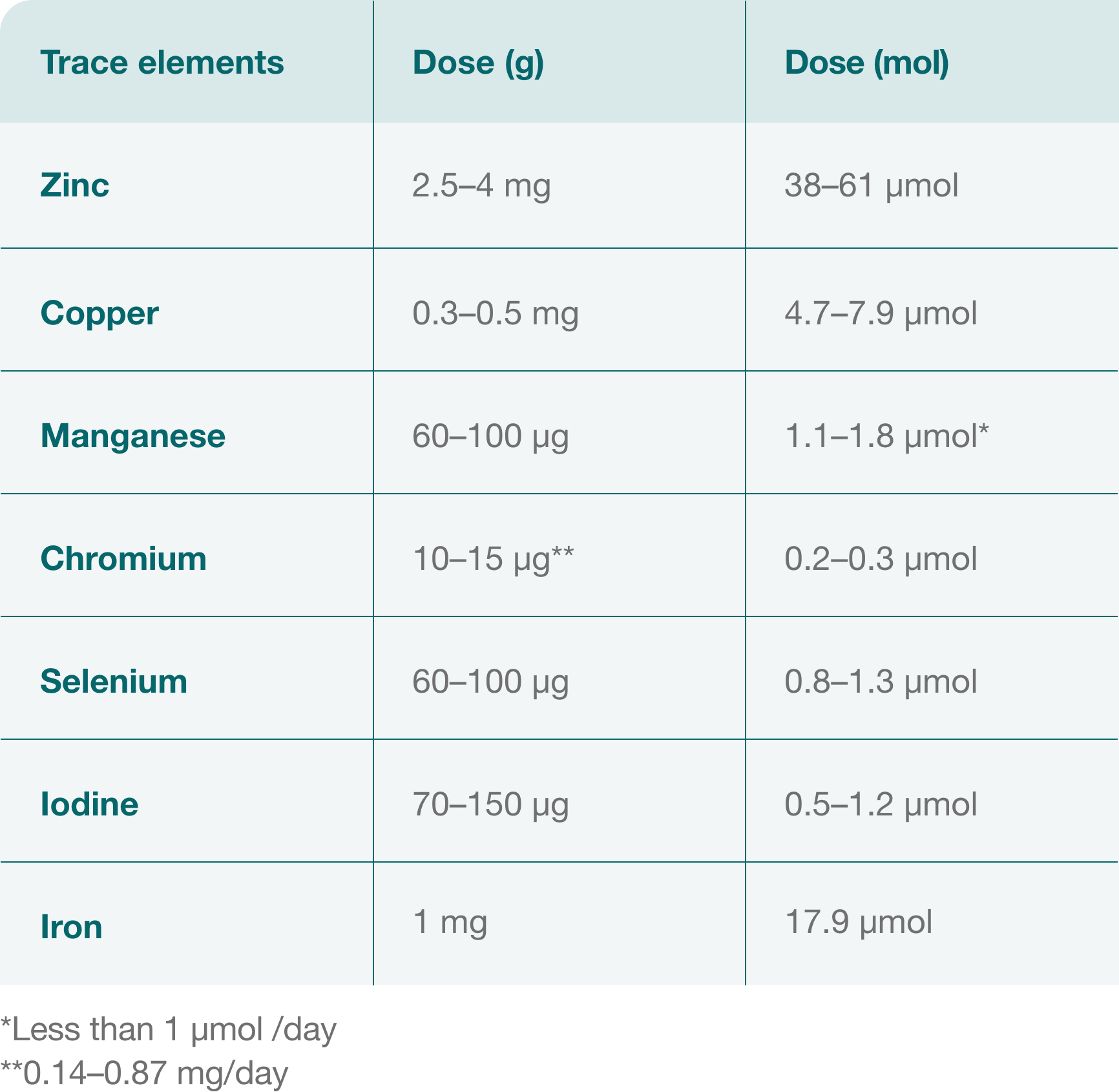
The following are recommended daily doses of trace elements for parenteral nutrition:1,2,10-12
All types of PN can cause side effects and may not be suitable for everyone, so it’s important to discuss options with the SBS specialist team.
References:
- Pironi L, Cuerda C, Jeppesen PB, et al. ESPEN guideline on chronic intestinal failure in adults – Update 2023. Clin Nutr. 2023 Oct;42(10):1940-2021.
- Fresenius Kabi Canada Ltd. SmofKabiven (amino acids with electrolytes, dextrose and lipid injectable emulsion) Product Monograph. July 9, 2020.
- Baxter Corporation. CLINIMIX Blend B (amino acids without electrolytes in dextrose injection) Product Monograph. April 1, 2022.
- Baxter Corporation. CLINIMIX Blend CD (amino acids without electrolytes in dextrose injection) Product Monograph. March 31, 2022.
- Baxter Corporation. CLINIMIX E Blend B (amino acids without electrolytes in dextrose injection) Product Monograph. March 31, 2022.
- Fresenius Kabi Canada Ltd. SMOFlipid 20% (lipid injection emulsion) Product Monograph. July 5, 2023.
- Baxter Corporation. CLINOLEIC (refined olive oil and refined soybean oil lipid emulsion) 20% Product Monograph. July 30, 2014.
- Baxter Corporation. 20% Dextrose Injection, USP, 50% Dextrose Injection, USP and 70% Dextrose Injection, USP Product Monograph. November 21, 2018.
- Baxter Corporation. 50% Dextrose Injection, USP and 70% Dextrose Injection, USP Product Monograph. November 21, 2018.
- Fresenius Kabi Canada Ltd. Addnutriv (trace elements for injection) Product Monograph. March 31, 2020.
- Sandoz Canada Inc. MICRO +4 REGULAR STRENGTH 4 (trace elements injection) Product Monograph. April 25, 1994.
- Baxter Corporation. TRAVASOL E (amino acids (blend B) WITH electrolytes injection 10% w/v) Product Monograph. April 1, 2020.

